A C/AL statement is a code instruction that when it is executed, causes operations to occur, which can change one or more variables or initiate read and write transactions to the database.
A C/AL statement is built from expressions.
A C/AL expression is a group of characters (data values, variables, arrays, operators, and functions) that can be evaluated, with the result having an associated data type. An expression is a fundamental C/AL concept. All expressions in C/AL are built from the following:
-
Constants
-
Variables
-
Operators
-
Functions
-
Keywords
For more information about constants, variables, operators, functions, and keywords, see Elements of C/AL Expressions.
Example 1
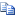
For this example, consider the following C/AL code.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
Amount := 34 + Total; | |
This line of code is also called a statement. The following table illustrates how the statement can be broken into smaller elements.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
34 + Total | An expression. This expression consists of an arithmetic operator (+) and two arguments (34 and Total), which could also be called sub-expressions. Every valid C/AL expression can be evaluated to a specific value. |
:= | The assignment operator. When the expression on the right side has been evaluated, this operator is used to assign or store the value in the variable on the left side. |
Amount | A variable. Used to reference a memory location where data is stored. |
Example 2
An expression can be used as an argument for a C/AL function. Consider the following C/AL statement.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
Date := DMY2DATE(31, 12, 2001); | |
This function takes three simple expressions as arguments: 31, 12, and 2001.
Typical Expressions
Depending on the elements in the expression, the evaluation gives you a value with a C/AL data type. The following table shows some typical expressions.
| Expression | Evaluates to | Description |
|---|---|---|
'Welcome to Hawaii' | The string 'Welcome to Hawaii' | Evaluates to itself. |
'Welcome ' + 'to Hawaii' | The string 'Welcome to Hawaii' | Evaluates to a concatenation of the two strings. |
43.234 | The number 43.234 | Evaluates to itself, a decimal number. |
ABS(-7234) | The number 7234 | A function that evaluates to a number. |
len1 < 618 | TRUE or FALSE, depending on the value of len1 | A comparison between a variable and a numeric constant, which evaluates to a Boolean value. |
These examples show that when C/AL expressions are evaluated, the results have a specific data type. For more information about data types, see C/AL Data Types.




